The treatment of arthrosis involves an integrated approach and a combination of different methods. Most treatment tactics consist of the correct prescription of medications. They can be integrated with traditional medicine methods.
Main trends in the modern treatment of osteoarthritis
After a comprehensive examination, which includes the main and accompanying diagnosis, appropriate treatment for arthrosis begins.
It includes the following methods:
- lifestyle modification;
- drug correction;
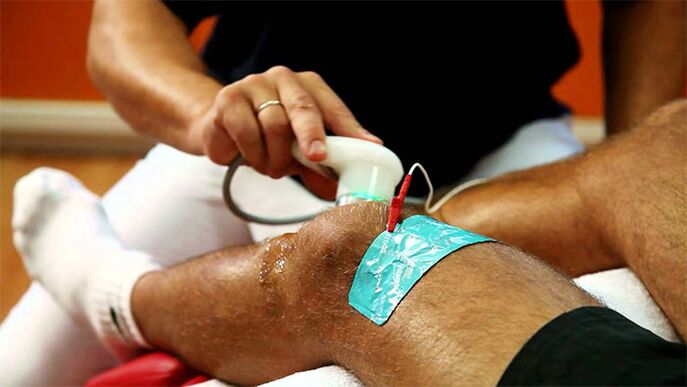
- Physiotherapy;
- surgery.
The choice of method depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of destruction of the joint structures. First, you should learn the following rules that will make the treatment more effective:
- Body weight correction;
- Physical therapy – exercises that eliminate the static load on the joint;
- Increase the level of knowledge of the pathology in patients;
- The use of additional accessories (joint bandages, insoles, stick or orthoses);
- Physiotherapy.
The diagnosis is carried out by an orthopedic-traumatologist. However, other specialists providing consultations can participate in this process:
- neurologist: consultation is necessary in case of damage to the intervertebral structures, radicular syndrome, severe back pain due to the disease;
- infectious disease specialist: exclusion of the infectious nature of joint disease;
- oncologist: exclusion of malignant neoplasms of bone and joint tissue or metastases in these areas;
- Osteophthisiatrician: exclude the tuberculous nature of the bone lesions.
During the disease, prevention of complications of the pathology and its progression is carried out. To do this, you need to use orthotics and fix bandages, monitor body weight, nutrition and regularly consult a doctor. Consultations with a treating specialist are necessary at least 2 times a year.
The effectiveness of the treatment meets the following criteria:
- Stop the progression of the disease;
- The new joints are not involved in the pathological process;
- The pain decreases or disappears;
- There are no signs of an inflammatory process;
- Quality of life, motor activity and ability to work improve.
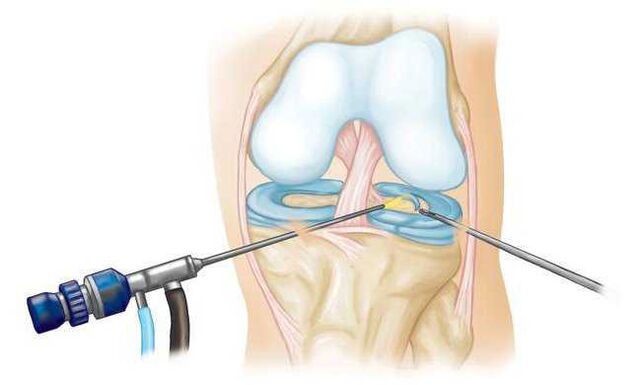
On the contrary, there are features of the course of the disease that require hospitalization and correction of tactics for recovery:
- persistent and intense pain syndrome;
- severe inflammation of the joint and periarticular structures (the skin over the affected area is hot to the touch, redness, increase in size, pain and limitation of movement are observed).
Medicines
The choice of a drug complex depends on the stage of the process:
- Phase I – non-drug correction methods, non-steroidal drugs and drugs that strengthen cartilage tissue;
- Stage II – non-drug correction methods, non-steroidal drugs and drugs that strengthen cartilage tissue, intra-articular administration of maintenance therapy;
- Stage III – non-drug correction methods, non-steroidal drugs and drugs that strengthen cartilage tissue, intra-articular administration of maintenance therapy, antidepressants;
- Stage IV – radical surgery involving excision of the affected tissue and installation of an artificial joint.
Also, in case of severe pain, analgesics are used, and various ointments can be used to eliminate severe inflammation of the soft tissues.
Treatment of arthrosis is carried out according to established courses, the duration of which cannot be violated independently. Even if the situation seems to have improved, it is necessary to continue taking the drug, because it tends to accumulate in the body. Likewise, it is not possible to independently adjust the dose of the drug, either in the direction of decreasing or increasing it.
The drugs must be taken at the same time every day. Features of reception - according to the instructions. If the patient is being treated for another pathology, the doctor must analyze the combined effect of all drugs and exclude dangerous combinations.
Drugs
Let's look at the main groups and examples of drugs.
Examples are provided; the attending physician may prescribe other representatives of these groups of drugs.
- Analgesics.They are used to relieve pain, allowing you to restore freedom of movement and improve quality of life.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.They reduce joint pain, eliminate swelling and redness of soft tissues, normalize the temperature of the skin over the joint and restore freedom of movement.
- Chondroprotectors.They contain elements of animal cartilaginous tissue, which allow you to restore the structure of the joint, periarticular surfaces, ligaments and synovium. It slows down the progression of the process and strengthens healthy joints.
- Narcotic analgesic.Used for emergency relief in severe pain. Duration of hospitalization: once, if necessary.
- Hyaluronic acid derivatives.A viscous implant containing hyaluronic acid is inserted intra-articularly. Improves the condition of the ligaments, synovium and soft tissues. It allows water retention, improves the condition of collagen fibers, making tissues elastic, resistant to injury and destruction.
- Glucocorticosteroids.Used for severe inflammation. They allow you to effectively influence the pathology and act quickly.
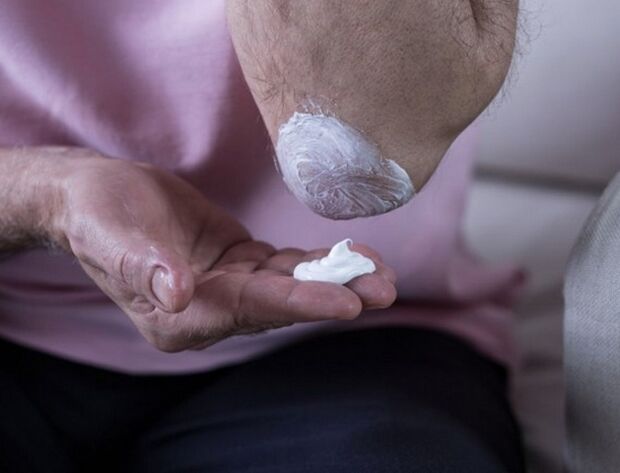
Use of ointments
Treatment of arthrosis involves the use of ointments. In some cases, they alleviate the patient's condition by relieving pain. However, this only makes sense in the early stages of the pathology. The fact is that any drug taken by the patient orally is absorbed into the bloodstream in the digestive tract and through it acts on the joint tissue. If intravascular administration is used, the effect can be achieved more quickly and the effect on the mucosa is also eliminated.
Applying the drug in the form of an ointment or gel causes the drug to act only on the skin and a small layer of soft tissue underneath. The patient must understand that it does not affect the joint, but only acts symptomatically.
For this purpose, the following ointments are used:
- containing non-steroidal drugs;
- containing salicylic acid;
- containing capsaicin.
It can also be an ointment or gel based on medicinal plants, which improve the condition of soft tissues and reduce sensitivity. It can be an ointment with menthol, camphor, eucalyptus or peppermint.

Traditional methods of treating arthrosis
Folk remedies imply the alleviation of pathological syndromes. It is not possible to achieve full recovery from an illness using such techniques; they are used in parallel with therapy and physical procedures. If you take only homemade drugs, the disease can progress and the patient will only waste time.
The following drugs have a symptomatic effect:
- grated horseradish root compress. Used daily, in a cycle of 7-9 days. A film and a warm cloth are placed over the root pulp. The duration of the compress is 30 minutes;
- An oatmeal compress is used according to a similar principle. For this, a creamy flake paste is prepared. After the mixture has cooled, it is applied to the joint;
- The honey compress can be left overnight. It is preferable to use wild honey;
- A cabbage leaf with a layer of honey is applied to the affected joint. Repair and leave overnight;
- mix the chalk powder with the thick yogurt. Apply to the joint, wrap with film and top with a warm natural cloth. Leave the compress overnight.
Diagnostics
Effective treatment of osteoarthritis is possible with a correct diagnosis. For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- clinical diagnosis, which includes the results of examination and questioning of the patient;
- X-ray diagnostics, for which a healthy and affected joint is examined and their condition is compared;
- laboratory methods that allow you to exclude other causes of pathology;
- synovial fluid analysis;
- ultrasound examination for soft tissue inflammation;
- tomography for a more detailed study of soft tissues and periarticular structures.
























